1
GATE CSE 2009
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
Given the following state table of an $$FSM$$ with two states $$A$$ and $$B,$$ one input and one output:
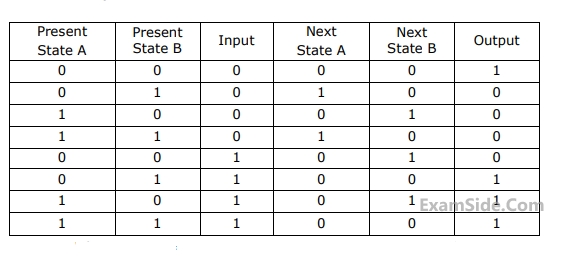

If the initial state is $$A = 0, B=0.$$ What is the minimum length of an input string which will take the machine to the state $$A=0, B=1$$ with Output$$=1?$$
2
GATE CSE 2007
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
The control signal functions of a $$4$$-bit binary counter are given below $$($$where $$X$$ “don’t care”$$):$$
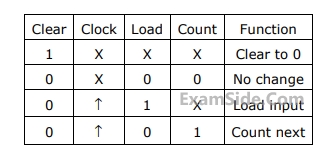
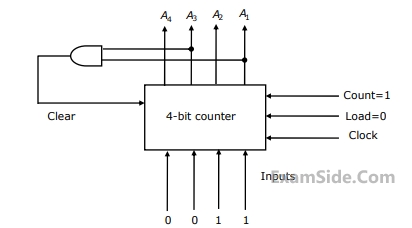

The counter is connected as follows:

Assume that the counter and gate delays are negligible. If the counter starts at $$0,$$ then it cycles through the following sequence:
3
GATE CSE 2006
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
Consider the circuit in the diagram. The $$ \oplus $$ operator represents $$EX$$-$$OR.$$ The $$D$$ flip-flops are initialized to zeros (cleared).
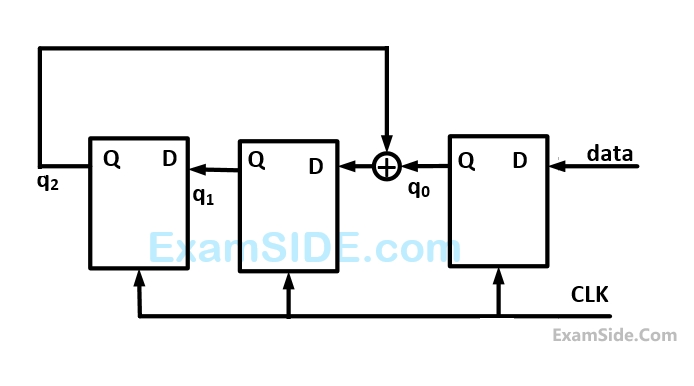

The following data: $$100110000$$ is supplied to the ''data'' terminal in nine clock cycles. After that the values of $${q_2}{q_1}{q_0}$$ are
4
GATE CSE 2004
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
Consider the partial implementation of a $$2$$-bit counter using $$T$$ flip-flops following the sequence $$0$$-$$2$$-$$3$$-$$1$$-$$0,$$ as shown below.


To complete the circuit, the input $$X$$ should be
Questions Asked from Marks 2
GATE CSE 2025 Set 1 (1) GATE CSE 2023 (1) GATE CSE 2022 (1) GATE CSE 2021 Set 2 (1) GATE CSE 2021 Set 1 (1) GATE CSE 2015 Set 1 (1) GATE CSE 2014 Set 3 (1) GATE CSE 2011 (2) GATE CSE 2009 (1) GATE CSE 2007 (1) GATE CSE 2006 (1) GATE CSE 2004 (1) GATE CSE 2003 (1) GATE CSE 2001 (2) GATE CSE 2000 (1) GATE CSE 1991 (1)
GATE CSE Subjects
Theory of Computation
Operating Systems
Algorithms
Digital Logic
Database Management System
Data Structures
Computer Networks
Software Engineering
Compiler Design
Web Technologies
General Aptitude
Discrete Mathematics
Programming Languages
Computer Organization