1
GATE CSE 2008
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
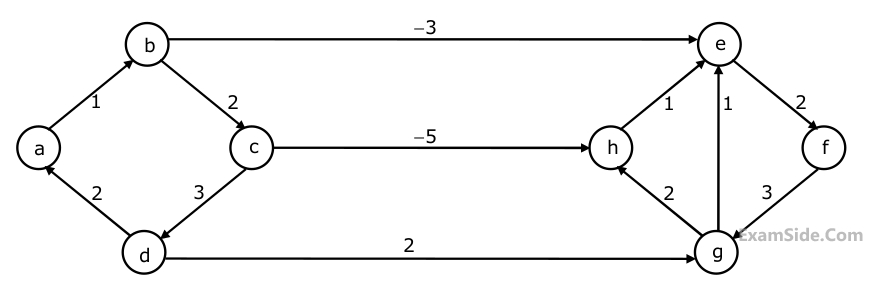 Dijkstra's single source shortest path algorithm when run from vertex a in the above graph, computes the correct shortest path distance to
Dijkstra's single source shortest path algorithm when run from vertex a in the above graph, computes the correct shortest path distance to2
GATE CSE 2007
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
Let w be the minimum weight among all edge weights in an undirected connected graph. Let e be a specific edge of weight w . Which of the following is FALSE?
3
GATE CSE 2007
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
Suppose the letters a, b, c, d, e, f have probabilities 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, 1/32, 1/32 respectively. What is the average length of Huffman codes?
4
GATE CSE 2007
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
In an unweighted, undirected connected graph, the shortest path from a node S to every other node is computed most efficiently, in terms of time complexity by
Questions Asked from Marks 2
GATE CSE 2025 Set 2 (1) GATE CSE 2025 Set 1 (1) GATE CSE 2024 Set 2 (2) GATE CSE 2021 Set 2 (1) GATE CSE 2020 (2) GATE CSE 2018 (2) GATE CSE 2016 Set 1 (2) GATE CSE 2015 Set 2 (1) GATE CSE 2015 Set 1 (1) GATE CSE 2014 Set 2 (2) GATE CSE 2012 (1) GATE CSE 2011 (2) GATE CSE 2010 (2) GATE CSE 2009 (1) GATE CSE 2008 (1) GATE CSE 2007 (4) GATE CSE 2006 (1) GATE CSE 2004 (1) GATE CSE 2003 (3) GATE CSE 2000 (1) GATE CSE 1992 (1) GATE CSE 1991 (2)
GATE CSE Subjects
Theory of Computation
Operating Systems
Algorithms
Digital Logic
Database Management System
Data Structures
Computer Networks
Software Engineering
Compiler Design
Web Technologies
General Aptitude
Discrete Mathematics
Programming Languages
Computer Organization