1
GATE CSE 1999
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
System calls are usually invoked by using:
2
GATE CSE 1998
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
Consider $$n$$ processes sharing the $$CPU$$ in a round-robin fashion. Assuming that each process switch takes $$s$$ seconds, what must be the quantum size $$q$$ such that the overhead resulting from process switching is minimized but, at the same time each process is guaranteed to get its turn at the $$CPU$$ at least every $$t$$ seconds?
3
GATE CSE 1998
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
Which of the following is an example of spooled device?
4
GATE CSE 1996
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
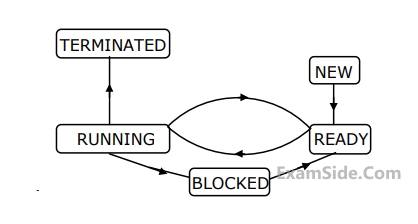
The process state transition diagram in Figure is representative of

Questions Asked from Marks 1
GATE CSE 2025 Set 2 (1) GATE CSE 2025 Set 1 (1) GATE CSE 2024 Set 2 (1) GATE CSE 2024 Set 1 (1) GATE CSE 2023 (2) GATE CSE 2021 Set 2 (1) GATE CSE 2021 Set 1 (1) GATE CSE 2020 (1) GATE CSE 2019 (1) GATE CSE 2016 Set 1 (1) GATE CSE 2015 Set 3 (1) GATE CSE 2014 Set 1 (1) GATE CSE 2013 (1) GATE CSE 2012 (1) GATE CSE 2011 (3) GATE CSE 2010 (1) GATE CSE 2009 (1) GATE CSE 2007 (2) GATE CSE 2006 (1) GATE CSE 2004 (1) GATE CSE 2002 (1) GATE CSE 2001 (3) GATE CSE 1999 (1) GATE CSE 1998 (2) GATE CSE 1996 (2) GATE CSE 1995 (1)
GATE CSE Subjects
Theory of Computation
Operating Systems
Algorithms
Digital Logic
Database Management System
Data Structures
Computer Networks
Software Engineering
Compiler Design
Web Technologies
General Aptitude
Discrete Mathematics
Programming Languages
Computer Organization