1
GATE CSE 2021 Set 2
Numerical
+2
-0
Consider a Boolean function f(w, x, y, z) such that
f(w, 0, 0, z) = 1
f(1, x, 1, z) = x + z
f(w, 1, y, z) = wz + y
The number of literals in the minimal sum-of-products expression of f is ______
Your input ____
2
GATE CSE 2021 Set 1
MCQ (More than One Correct Answer)
+2
-0
Consider the following Boolean expression.
$$F = (X + Y + Z)(\overline X + Y)(\overline Y + Z)$$
Which of the following Boolean expressions is/are equivalent to $$\overline F$$ (complement of F)?
3
GATE CSE 2020
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.67
Consider the Boolean function z(a,b,c).

Which one of the following minterm lists represents the circuit given above?

Which one of the following minterm lists represents the circuit given above?
4
GATE CSE 2019
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.67
Consider three 4-variable functions f1, f2 and f3, which are expressed in sum-of-minterms as
f1 = Σ(0, 2, 5, 8, 14),
f2 = Σ(2, 3, 6, 8, 14, 15),
f3 = Σ(2, 7, 11, 14)
For the following circuit with one AND gate and one XOR gate, the output function f can be expressed as :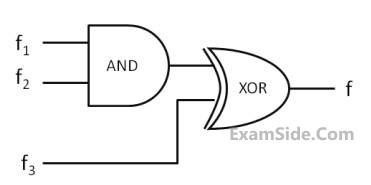
f1 = Σ(0, 2, 5, 8, 14),
f2 = Σ(2, 3, 6, 8, 14, 15),
f3 = Σ(2, 7, 11, 14)
For the following circuit with one AND gate and one XOR gate, the output function f can be expressed as :

Questions Asked from Marks 2
GATE CSE 2025 Set 2 (1) GATE CSE 2024 Set 2 (1) GATE CSE 2024 Set 1 (1) GATE CSE 2021 Set 2 (1) GATE CSE 2021 Set 1 (1) GATE CSE 2020 (1) GATE CSE 2019 (1) GATE CSE 2018 (1) GATE CSE 2016 Set 1 (1) GATE CSE 2015 Set 3 (2) GATE CSE 2015 Set 2 (2) GATE CSE 2015 Set 1 (2) GATE CSE 2014 Set 3 (1) GATE CSE 2010 (1) GATE CSE 2008 (1) GATE CSE 2007 (1) GATE CSE 2006 (1) GATE CSE 2004 (1) GATE CSE 2002 (3) GATE CSE 2000 (1) GATE CSE 1999 (1) GATE CSE 1997 (2) GATE CSE 1990 (1)
GATE CSE Subjects
Theory of Computation
Operating Systems
Algorithms
Digital Logic
Database Management System
Data Structures
Computer Networks
Software Engineering
Compiler Design
Web Technologies
General Aptitude
Discrete Mathematics
Programming Languages
Computer Organization