Computer Networks
1
GATE CSE 2016 Set 1
Numerical
+2
-0
An IP datagram of size 1000 bytes arrives at a router. The router has to forward this packet on a link whose MTU (maximum transmission unit) is 100 bytes. Assume that the size of the IP header is 20 bytes.
The number of fragments that the IP datagram will be divided into for transmission is ________.
Your input ____
2
GATE CSE 2015 Set 3
Numerical
+2
-0
In the network 200.20.11.144/27, the fourth octet (in decimal) of the last IP address of the network which can be assigned to a host is ________.
Your input ____
3
GATE CSE 2015 Set 2
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
Host A sends a UDP datagram containing 8880 bytes of user data to host B over an Ethernet LAN. Ethernet frames may carry data up to 1500 bytes (i.e. MTU = 1500 bytes). Size of UDP header is 8 bytes and size of IP heard is 20 bytes.There is no option field in IP header How many total number of IP fragments will be transmitted and what will be the contents of offset field in the last fragment?
4
GATE CSE 2015 Set 2
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
Consider the following routing table at an IP router:

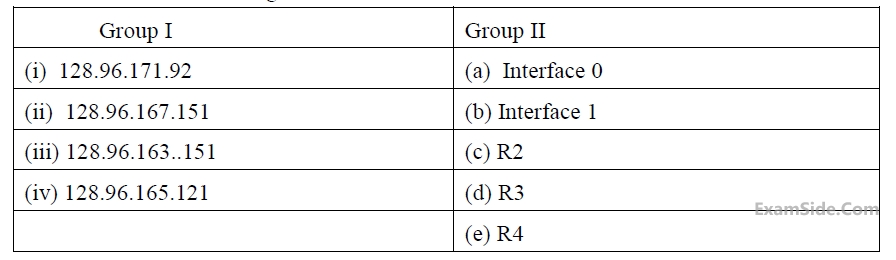

For each IP address in Group I identify the correct choice of the next hop from Group II using the entries from the routing table above.

Questions Asked from Marks 2
GATE CSE 2025 Set 1 (1) GATE CSE 2024 Set 2 (1) GATE CSE 2024 Set 1 (3) GATE CSE 2021 Set 2 (1) GATE CSE 2020 (1) GATE CSE 2019 (2) GATE CSE 2016 Set 1 (1) GATE CSE 2015 Set 3 (1) GATE CSE 2015 Set 2 (2) GATE CSE 2014 Set 3 (3) GATE CSE 2014 Set 2 (1) GATE CSE 2013 (1) GATE CSE 2012 (1) GATE CSE 2010 (1) GATE CSE 2008 (1) GATE CSE 2007 (1) GATE CSE 2006 (1) GATE CSE 2004 (1) GATE CSE 2003 (1)
GATE CSE Subjects
Theory of Computation
Operating Systems
Algorithms
Digital Logic
Database Management System
Data Structures
Computer Networks
Software Engineering
Compiler Design
Web Technologies
General Aptitude
Discrete Mathematics
Programming Languages
Computer Organization