Mechanics
Units & Measurement
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)Motion in a Straight Line
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)Laws of Motion
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)Work, Energy and Power
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)Center of Mass and Collision
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)Rotational Motion
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)Gravitation
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)Properties of Matter
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)Heat and Thermodynamics
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)Oscillations
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)Electricity
Electrostatics
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)Current Electricity
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)Capacitor
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)Moving Charges and Magnetism
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)Magnetism and Matter
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)Electromagnetic Induction
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)Electromagnetic Waves
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)Modern Physics
Atoms and Nuclei
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)Semiconductor Electronics
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)1
AIPMT 2015
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+4
-1
Two metal wires of identical dimensions are connected in series. If $$\sigma $$1 and $$\sigma $$2 are the conductivity of the combination is
2
AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+4
-1
A potentiometer wire has length 4 m and resistance 8 $$\Omega $$. The resistance that must be connected in series with the wire and an accumulator of e.m.f. 2 V, so as to get a potential gradient 1 mV per cm on the wire is
3
AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+4
-1
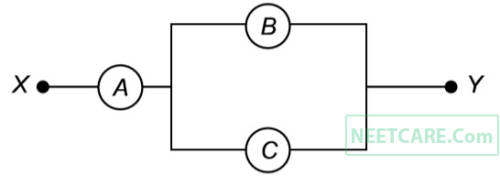
A, B and C are voltmeters of resistance R, 1.5 R and 3R respectively as shown in the figure. When some potential difference is applied between X and Y, the voltmeter readings are VA, VB and VC respectively, Then

4
AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+4
-1
Across a metallic conductor of non-uniform cross section a constant potential difference is applied. The quantity which remains constant along the conductor is
Questions Asked from MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
NEET 2025 (3) NEET 2024 (Re-Examination) (3) NEET 2024 (4) NEET 2023 Manipur (3) NEET 2023 (5) NEET 2022 Phase 2 (4) NEET 2022 Phase 1 (3) NEET 2021 (4) NEET 2020 Phase 1 (5) NEET 2019 (3) NEET 2018 (3) NEET 2017 (2) NEET 2016 Phase 2 (2) NEET 2016 Phase 1 (2) AIPMT 2015 (3) AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper (3) AIPMT 2014 (3) NEET 2013 (Karnataka) (3) NEET 2013 (3) AIPMT 2012 Mains (2) AIPMT 2012 Prelims (3) AIPMT 2011 Mains (2) AIPMT 2011 Prelims (2) AIPMT 2010 Prelims (2) AIPMT 2009 (4) AIPMT 2008 (5) AIPMT 2007 (2) AIPMT 2006 (4) AIPMT 2005 (4) AIPMT 2004 (6) AIPMT 2003 (4) AIPMT 2002 (2) AIPMT 2001 (3) AIPMT 2000 (4)
NEET Subjects
Physics
Mechanics
Electricity
Chemistry
Physical Chemistry
Inorganic Chemistry
Biology
Botany
Cell - The Unit of LifeBiomoleculesCell Cycle and Cell DivisionSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsMicrobes in Human WelfareAnatomy of Flowering PlantsTransport in PlantsMineral NutritionRespiration in PlantsBiotechnology: Principles and ProcessesBiodiversity and ConservationThe Living WorldBiological ClassificationMorphology of Flowering PlantsPhotosynthesis in Higher PlantsPrinciples of Inheritance and VariationMolecular Basis of InheritanceStrategies for Enhancement in Food ProductionBiotechnology and It's ApplicationsOrganisms and PopulationsEnvironmental IssuesPlant KingdomPlant Growth and DevelopmentEcosystem
Zoology
Human Health and DiseasesBody Fluids and Its CirculationLocomotion and MovementNeural Control and CoordinationReproduction in OrganismsReproductive HealthStructural Organisation in AnimalsDigestion and AbsorptionExcretory Products and Their EliminationChemical Coordination and IntegrationHuman ReproductionAnimal KingdomBreathing and Exchange of GasesEvolution