Analog Circuits
1
GATE ECE 2016 Set 2
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
Which one of the following statements is correct about an ac-coupled common- emitter amplifier operating in the mid-band region?
2
GATE ECE 2003
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
Generally, the gain of a transistor Amplifier falls at high frequency due to the
3
GATE ECE 2002
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
Three identical RC-Coupled transistor amplifiers are cascaded. If each of the
amplifiers has a frequency response as shown in figure, the overall frequency
response is as given as
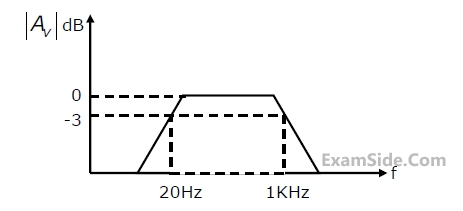

4
GATE ECE 2000
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
The current gain of a bipolar transistor drops at high frequencies because of
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics



