1
GATE ECE 2007
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
Two 4-ray signal constellations are shown. It is given that $${\phi _1}$$ and $${\phi _2}$$ constitute an orthonormal basis for the two constellations. Assume that the four symbols in both the constellations are equiprobable. Let $${{{N_0}} \over 2}$$ denote the power spectral density of white Gaussian noise.
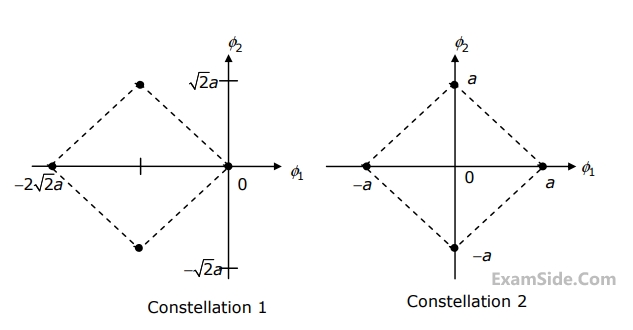

The ratio of the average energy of Constellation 1 to the average energy of Constellation 2 is
2
GATE ECE 2007
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
Two 4-ray signal constellations are shown. It is given that $${\phi _1}$$ and $${\phi _2}$$ constitute an orthonormal basis for the two constellations. Assume that the four symbols in both the constellations are equiprobable. Let $${{{N_0}} \over 2}$$ denote the power spectral density of white Gaussian noise.


If these constellations are used for digital communications over an AWGN channel, then which of the following statements is true?
3
GATE ECE 2006
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
Let $$g\left( t \right){\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} \,\,\,\,\,{\mkern 1mu} = {\mkern 1mu} {\mkern 1mu} p\left( t \right){}^ * p\left( t \right)$$ where $$ * $$ denotes convolution and $$p(t) = u(t) - u(t-1)$$ with $$u(t)$$ being the unit step function
The impulse response of filter matched to the signal $$s(t) = g(t)$$ $$ - \delta {\left( {t - 2} \right)^ * }\,\,g\left( t \right)$$ is given as:
4
GATE ECE 2006
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
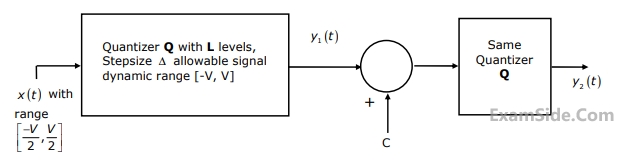
In the following figure the minimum value of the constant “C”, which is to be added to y1(t) such that y1(t) and y2(t) are different, is

Questions Asked from Marks 2
GATE ECE 2025 (1) GATE ECE 2016 Set 1 (2) GATE ECE 2015 Set 2 (1) GATE ECE 2015 Set 1 (2) GATE ECE 2014 Set 4 (2) GATE ECE 2014 Set 2 (1) GATE ECE 2013 (1) GATE ECE 2012 (2) GATE ECE 2011 (2) GATE ECE 2010 (2) GATE ECE 2009 (2) GATE ECE 2008 (1) GATE ECE 2007 (5) GATE ECE 2006 (2) GATE ECE 2005 (3) GATE ECE 2004 (1) GATE ECE 2003 (2) GATE ECE 2001 (1) GATE ECE 1999 (2) GATE ECE 1988 (2) GATE ECE 1987 (1)
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics