Digital Circuits
1
GATE ECE 2001
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
The digital block in the figure is realized using two positive edge triggered D flip-flops. Assume that for t < t0, Q1 = Q2 =0. The circuit in the digital block is given by


2
GATE ECE 2000
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
In the figure, the J and K inputs of all the four Flip-Flops are made high. The frequency of the signal at output Y is 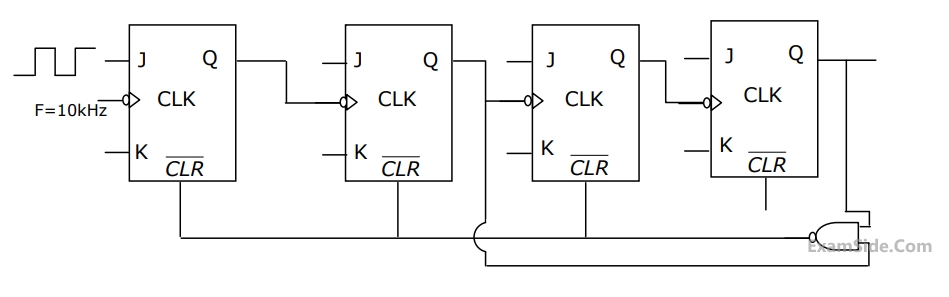

3
GATE ECE 2000
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A sequential circuit using D flip-flop and logic gates is shown in the figure, where X and Y are the inputs and Z is the output. The circuit is
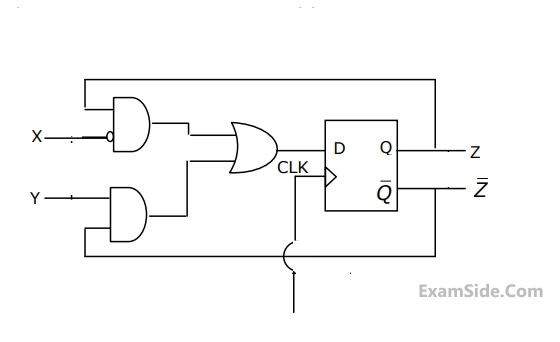

4
GATE ECE 1999
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
The ripple counter shown in the figure works as a


Questions Asked from Marks 2
GATE ECE 2025 (2) GATE ECE 2024 (1) GATE ECE 2023 (1) GATE ECE 2022 (2) GATE ECE 2018 (1) GATE ECE 2017 Set 2 (1) GATE ECE 2017 Set 1 (2) GATE ECE 2016 Set 2 (2) GATE ECE 2015 Set 2 (1) GATE ECE 2015 Set 3 (2) GATE ECE 2014 Set 1 (1) GATE ECE 2014 Set 2 (2) GATE ECE 2012 (1) GATE ECE 2011 (2) GATE ECE 2009 (1) GATE ECE 2008 (1) GATE ECE 2007 (2) GATE ECE 2006 (1) GATE ECE 2004 (1) GATE ECE 2003 (1) GATE ECE 2001 (1) GATE ECE 2000 (2) GATE ECE 1999 (1) GATE ECE 1998 (1)
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics



