Network Theory
State Equations For Networks
Marks 51
GATE ECE 2012
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.33
The average power delivered to an impedance $(4-j 3) \Omega$ by a current $5 \cos (100 \pi t+100) A$ is
2
GATE ECE 2009
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
In the interconnection of ideal sources shown in the figure, it is known that the 60V source is absorbing power.

Which of the following can be the value of the current source I?
3
GATE ECE 2004
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
The equivalent inductance measured between the terminals 1 and 2 for the circuit shown in figure, is

4
GATE ECE 2002
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
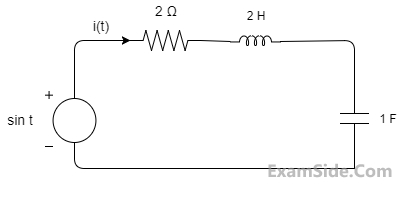
The differential equation for the current i(t) in the circuit of Fig. is
Questions Asked from Marks 1
GATE ECE 2022 (2) GATE ECE 2021 (1) GATE ECE 2017 Set 2 (1) GATE ECE 2015 Set 1 (1) GATE ECE 2014 Set 4 (1) GATE ECE 2014 Set 3 (1) GATE ECE 2014 Set 1 (1) GATE ECE 2013 (1) GATE ECE 2012 (3) GATE ECE 2009 (1) GATE ECE 2004 (1) GATE ECE 2002 (2) GATE ECE 2001 (1) GATE ECE 2000 (2) GATE ECE 1998 (2) GATE ECE 1997 (4) GATE ECE 1995 (1) GATE ECE 1993 (1)
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics