Network Theory
State Equations For Networks
Marks 51
GATE ECE 2023
Numerical
+1
-0
In the circuit shown below, switch S was closed for a long time. If the switch is opened at t = 0, the maximum magnitude of the voltage $$\mathrm{V_R}$$, in volts, is __________ (rounded off to the nearest integer).

Your input ____
2
GATE ECE 2016 Set 2
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
The switch has been in position 1for a long time and abruptly changes to position 2 at t = 0.
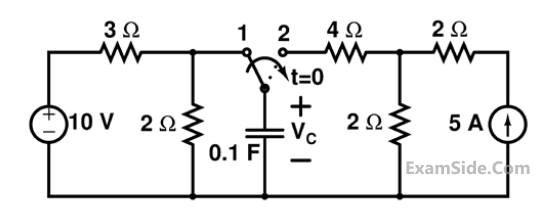 If time t is in seconds, the capacitor voltage VC (in volts) for t>0 is given by
If time t is in seconds, the capacitor voltage VC (in volts) for t>0 is given by
 If time t is in seconds, the capacitor voltage VC (in volts) for t>0 is given by
If time t is in seconds, the capacitor voltage VC (in volts) for t>0 is given by3
GATE ECE 2015 Set 1
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
In the circuit shown, the switch SW is thrown from position A to position B at time t = 0. The
energy (in $$\mu J$$) taken from the 3V source to charge the 0.1$$\mu$$F capacitor from 0V to 3V is
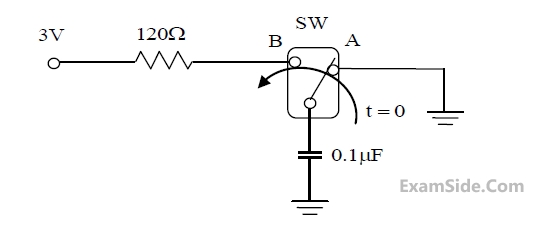

4
GATE ECE 2014 Set 3
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
A series RC circuit is connected to a DC voltage source at time t = 0. The relation between the source voltage VS, the resistance R, the capacitance C, and the current i(t) is given below:
$$$V_{s\;}=\;Ri(t)+\frac1c\int_0^ti(u)du$$$
Which one of the following represents the current f(t)?
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics



