Power System Analysis
High Voltage Dc Transmission
Marks 11
GATE EE 1999
Subjective
+5
-0
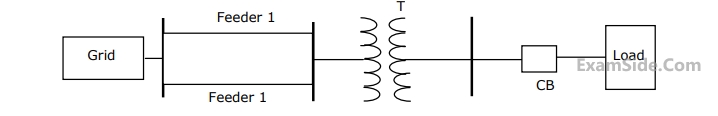
Determine the required MVA rating of the circuit breaker CB for the system shown in given figure. Consider the grid as infinite bus. Choose 6 MVA as base. Transformer 3-phase, 33/11 kV, 6 MVA, 0.01+j0.08 p.u. impedance. Load 3-phase 11 kV, 5800 kVA, 0.8 lag, j0.2 p.u. impedance. Impedance of each feeder 9+j 18 $$\Omega $$.

2
GATE EE 1999
Subjective
+5
-0
Determine the magnitudes of the symmetrical components ($${{{\rm I}_{R1}},\,{{\rm I}_{R2}}\,}$$ and $${{{\rm I}_{R0}}}$$) of the currents in a three phase (RYB) three wire system, when a short circuit occurs between R and Y phase wires, the fault current being 100 A.
3
GATE EE 1994
True or False
+5
-0
In a power-system, the $$3$$-phase fault MVA is always higher than the single-line-ground fault MVA at a bus (State True or False)
Questions Asked from Marks 5
GATE EE Subjects
Electromagnetic Fields
Signals and Systems
Engineering Mathematics
General Aptitude
Power Electronics
Power System Analysis
Analog Electronics
Control Systems
Digital Electronics
Electrical Machines
Electric Circuits
Electrical and Electronics Measurement