Signals and Systems
1
GATE ECE 2014 Set 2
Numerical
+2
-0
Consider a discrete-time signal
$$x\left[ n \right] = \left\{ {\matrix{ {n\,\,for\,\,0 \le n \le 10} \cr {0\,\,otherwise} \cr } } \right.$$
$$x\left[ n \right] = \left\{ {\matrix{ {n\,\,for\,\,0 \le n \le 10} \cr {0\,\,otherwise} \cr } } \right.$$
If $$y\left[ n \right]$$ is the convolution of $$x\left[ n \right]$$ with itself, the value of $$y\left[ 4 \right]$$ is
Your input ____
2
GATE ECE 2012
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
Let $$y\left[ n \right]$$ denote the convolution of $$h\left[ n \right]$$ and $$g\left[ n \right]$$, where $$h\left[ n \right]$$ $$ = \,{\left( {1/2} \right)^2}\,\,u\left[ n \right]$$ and $$g\left[ n \right]\,$$ is a causal sequence. If $$y\left[ 0 \right]\,$$ $$ = \,1$$ and $$y\left[ 1 \right]\,$$ $$ = \,1/2,$$ then $$g\left[ 1 \right]$$ equals
3
GATE ECE 2011
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
Two system $${H_1}\left( z \right)$$ and $${H_2}\left( z \right)$$ are connected in cascade as shown below. The overall output $$y\left( n \right)$$ is the same as the input $$x\left( n \right)$$ with a one unit delay. The transfer function of the second system $${H_2}\left( z \right)$$ is
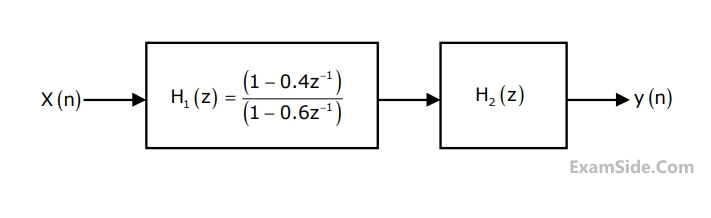

4
GATE ECE 2010
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
The transfer function of a discrete time LTI system is given by
$$H\left( z \right) = {{2 - {3 \over 4}{z^{ - 1}}} \over {1 - {3 \over 4}{z^{ - 1}} + {1 \over 8}{z^{ - 2}}}}$$
$$H\left( z \right) = {{2 - {3 \over 4}{z^{ - 1}}} \over {1 - {3 \over 4}{z^{ - 1}} + {1 \over 8}{z^{ - 2}}}}$$
Consider the following statements:
S1: The system is stable and causal for $$ROC:\,\,\,\left| z \right| > \,1/2$$
S2: The system is stable but not causal for $$ROC:\,\,\,\left| z \right| < \,1/4$$
S3: The system is neither stable nor causal for $$ROC:\,\,1/4\, < \,\left| z \right| < \,{\raise0.5ex\hbox{$\scriptstyle 1$}
\kern-0.1em/\kern-0.15em
\lower0.25ex\hbox{$\scriptstyle 2$}}$$
Which one of the following statements is valid?
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics