Network Theory
State Equations For Networks
Marks 51
GATE ECE 2014 Set 2
Numerical
+2
-0
A series LCR circuit is operated at a frequency different from its resonant frequency. The
operating frequency is such that the current leads the supply voltage. The magnitude of
current is half the value at resonance. If the values of L, C and R are 1 H, 1 F and 1Ω ,
respectively, the operating angular frequency (in rad/s) is ________.
Your input ____
2
GATE ECE 2014 Set 1
Numerical
+2
-0
In the circuit shown in the figure, the value of capacitor C (in mF) needed to have critically damped response i(t) is ______.


Your input ____
3
GATE ECE 2014 Set 1
Numerical
+2
-0
A periodic variable x is shown in the figure as a function of time. The root - mean - square (rms) value of x is _______ .
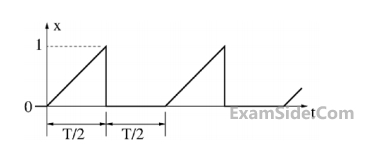

Your input ____
4
GATE ECE 2014 Set 1
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A 230 V rms source supplies power to two loads connected in parallel. The first load draws
10 kW at 0.8 leading power factor and the second one draws 10 kVA at 0.8 lagging power
factor. The complex power delivered by the source is
Questions Asked from Marks 2
GATE ECE 2025 (1) GATE ECE 2022 (2) GATE ECE 2018 (1) GATE ECE 2017 Set 1 (2) GATE ECE 2016 Set 1 (2) GATE ECE 2015 Set 1 (2) GATE ECE 2015 Set 3 (1) GATE ECE 2014 Set 4 (1) GATE ECE 2014 Set 3 (1) GATE ECE 2014 Set 2 (1) GATE ECE 2014 Set 1 (3) GATE ECE 2010 (1) GATE ECE 2009 (1) GATE ECE 2007 (2) GATE ECE 2005 (1) GATE ECE 2004 (2) GATE ECE 2003 (2) GATE ECE 2002 (1) GATE ECE 2001 (1) GATE ECE 2000 (1) GATE ECE 1993 (1) GATE ECE 1992 (1) GATE ECE 1991 (1) GATE ECE 1990 (2) GATE ECE 1989 (1) GATE ECE 1987 (1)
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics