Signals and Systems
1
GATE ECE 2000
Subjective
+5
-0
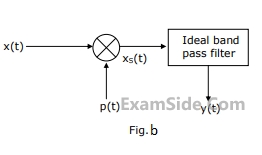
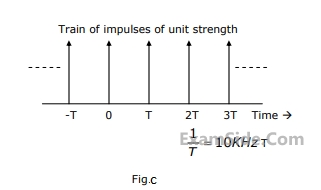
A band limited signal x(t) with a spectrum X(f) as shown in Fig. a is processed as shown in Fig.b. p(t) is a periodic train of impulses as in Fig. c. The ideal band pass filter has a pass band from 26 KHz to 34 KHz.
(a) Calculate the Fourier series coefficients $${c_n}$$ in the Fourier expansion of p(t) in form $$p(t) = \sum\limits_{n = - \infty }^{ + \infty } {{c_n}} \,\exp \,\,(j\,n\,2\pi \,t/T)$$.
(b) Find the Fourier Transform of p(t).
(c) Obtain and sketch the spectrum of $${x_s}(t)$$.
(d) Obtain and sketch the spectrum of y(t).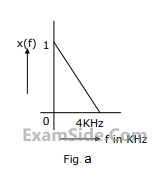
(a) Calculate the Fourier series coefficients $${c_n}$$ in the Fourier expansion of p(t) in form $$p(t) = \sum\limits_{n = - \infty }^{ + \infty } {{c_n}} \,\exp \,\,(j\,n\,2\pi \,t/T)$$.
(b) Find the Fourier Transform of p(t).
(c) Obtain and sketch the spectrum of $${x_s}(t)$$.
(d) Obtain and sketch the spectrum of y(t).



2
GATE ECE 1993
Subjective
+5
-0
A low pass signal m(t) band-limited to B Hz is sampled by a periodic rectangular pulse train, $${p_\tau }(t)$$ of period $${T_s}$$ = 1/(3B) sec. Assuming natural sampling and that the pulse amplitude and pulse width are A volts and 1/(30B) sec, respectively, obtain an expression for the frequency spectrum of the sampled signal $${m_s}$$(t)
Questions Asked from Marks 5
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics