Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier SeriesFourier TransformContinuous Time Signal Laplace TransformDiscrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier TransformDiscrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier TransformDiscrete Time Signal Z TransformContinuous Time Linear Invariant SystemDiscrete Time Linear Time Invariant SystemsTransmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI SystemsSamplingTransmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti SystemsMiscellaneousTransmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems
Practice QuestionsMarks 1
1
A causal and stable LTI system with impulse response h(t) produces an output y(t) for an input signal x(t). A signal x(0.5t) is applied to another causal and stable LTI system with impulse response h(0.5t). The resulting output is ____.
GATE ECE 2024
2
Consider a four-point moving average filter defined by the equation $$y[n] = \sum\limits_{i = 0}^3 {{\alpha _i}x[n - i]} $$. The condition on the filter coefficients that results in a null at zero frequency is
GATE ECE 2015 Set 3
Marks 2
1
The direct form structure of an FIR (finite impulse response) filter is shown in the figure.
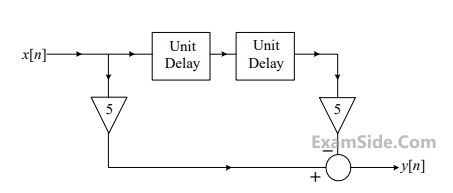

The filter can be used to approximate a
GATE ECE 2016 Set 3
2
A system with transfer function H(z) has impulse response h(.) defined as h(2) = 1, h(3) = - 1 and h (k) = 0 otherwise. Consider the following statements.
S1: H(z) is a low-pass filter.
S2: H(z) is an FIR filter.
S1: H(z) is a low-pass filter.
S2: H(z) is an FIR filter.
Which of the following is correct?
GATE ECE 2009
3
A signal x(n)$$ = \sin ({\omega _0}\,n + \phi )$$ is the input to a linear time-invariant system having a frequency response $$H({e^{j\omega }})$$.If the output of the system is $$Ax(n - {n_0})$$, then the most general form of $$\angle H({e^{j\omega }})$$ will be
GATE ECE 2005