Signals and Systems
1
GATE ECE 1995
Subjective
+5
-0
A sinsoidal signal, v(t) = A sin(t), is applied to an ideal full-wave rectifier. Show that the Laplace Transform of the output can be written in the form, $${V_0}\left( s \right) = {A \over {{s^2} + 1}}Coth\left( {\alpha s} \right),$$
where α is a constant. Determine the value of α.
2
GATE ECE 1991
Subjective
+5
-0
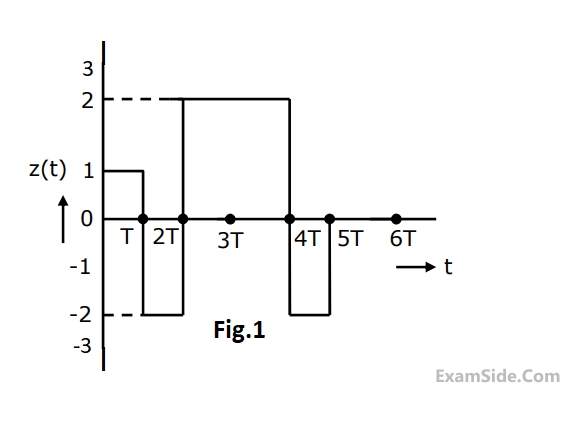
Find the Laplace transform of the waveform x(t) shown in Fig.1.

Questions Asked from Marks 5
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics